In today’s tech-driven world, Embedded Software Development has become a foundational part of industries and consumer products alike. From smart home appliances to life-saving medical equipment, embedded systems are powering innovation across the globe.
These systems combine hardware and software to perform dedicated functions within larger devices or environments. Unlike general-purpose software, embedded software must be optimized for performance, efficiency, and real-time response under limited hardware resources.
As the complexity of applications grows, so does the need for robust tools and frameworks to support developers in building fast, stable, and scalable embedded solutions. This article explores the best tools that streamline Embedded Software Development, improve productivity, and ensure project success.
What is Embedded Software?
Embedded software is specialized programming designed to operate hardware-specific functions. These software applications are not meant to run on general-purpose computers but are built for devices like sensors, automotive systems, medical instruments, and consumer electronics.
Embedded software plays a central role in IoT (Internet of Things), and is used across sectors such as automotive, telecommunications, healthcare, aerospace, and manufacturing.
The complexity of embedded software varies depending on the system’s purpose. Some applications require real-time processing, safety compliance, or low-power optimization. Unlike traditional software, it is written for a fixed set of functions tailored to a specific device, meaning it must be highly efficient and stable.
IDEs for Embedded Software Development
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) help consolidate the tools needed for coding, testing, and debugging into a single user interface, making the Embedded Software Development process smoother and more productive.
Visual Studio is one of the most widely used IDEs developed by Microsoft. It offers deep integration with Visual C++ and advanced debugging features, making it ideal for complex embedded projects.
Eclipse is another powerful IDE that originally targeted Java but now supports C, C++, and Python through plug-ins. Its modular design allows developers to tailor the environment based on their embedded project needs.
NetBeans, although primarily Java-focused, also provides support for C and C++, making it useful for embedded developers who work with multiple programming languages. Its integrated tools for code editing and debugging simplify development workflows.
PyCharm is tailored for Python development but supports cross-platform projects. It assists in project management and highlights syntax errors, making it suitable for embedded systems that leverage Python scripting.
Frameworks and Tools for Embedded Development

A variety of development platforms and frameworks exist to streamline Embedded Software Development, each catering to specific types of hardware and use cases.
Arduino offers an open-source environment that simplifies microcontroller programming. It is favored by both professionals and beginners due to its ease of use, wide compatibility, and strong community support.
Raspberry Pi is a flexible, low-cost single-board computer that supports multiple operating systems and development environments. It is commonly used in robotics, home automation, and educational projects where embedded software plays a key role.
STM32 microcontrollers from STMicroelectronics are known for their performance and power efficiency. These chips support various communication protocols and are widely adopted in industrial and automotive applications.
ARM mbed provides a suite of tools for developing embedded systems on ARM Cortex-M microcontrollers. It includes an online compiler, a range of libraries, and community-driven resources for rapid development.
FreeRTOS is a lightweight real-time operating system kernel designed for embedded devices. It helps developers manage multiple tasks efficiently and ensures timely execution of critical operations in constrained environments.
JTAG is a hardware-level debugging interface used to test and program embedded systems. It provides deep access to the internals of a device, allowing engineers to pinpoint hardware-related issues effectively.
Keil MDK is a professional-grade development suite for ARM-based microcontrollers. It offers advanced debugging capabilities and a range of prebuilt libraries to accelerate embedded software delivery.
MPLAB X from Microchip Technology is a free IDE that supports C and assembly programming. It includes a built-in simulator and debugger and is highly compatible with various Microchip microcontrollers.
Qt Framework for Embedded UI Development
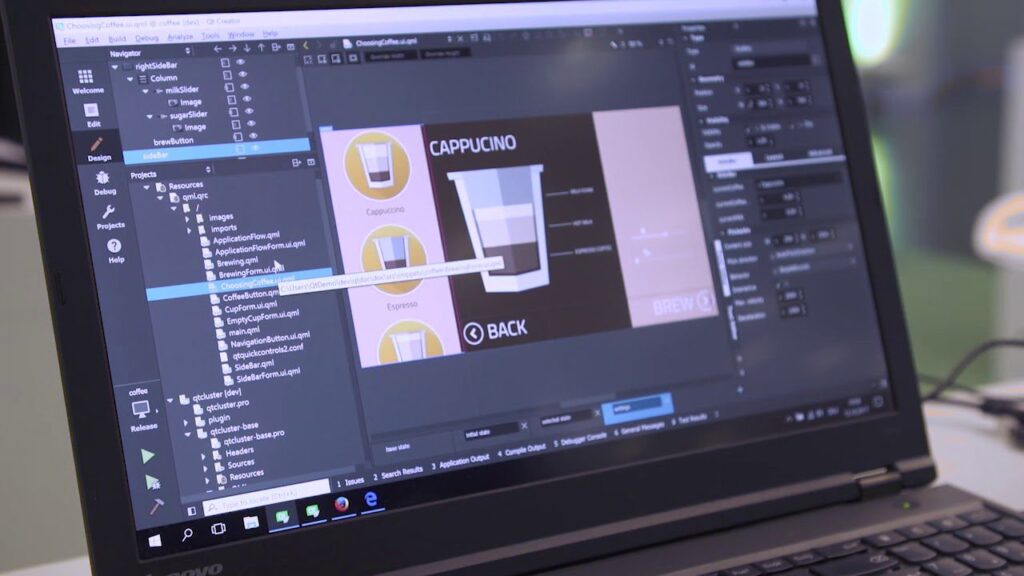
Qt is a highly versatile framework used in Embedded Software Development when building applications with or without graphical interfaces. Written in C++, it supports a wide range of devices and is particularly strong in creating responsive and visually engaging user interfaces.
Qt uses C++ for backend development and QML for frontend design, allowing developers to clearly separate logic from UI components. Its Qt Design Studio tool lets developers import design assets from third-party tools and rapidly convert them into fully functional user interfaces.
The Qt Creator IDE simplifies project management and debugging. Developers can easily connect embedded devices to a host machine, run tests, or debug code in real-time.
Qt for Embedded Linux extends the framework’s functionality for Linux-based embedded platforms, making it a popular choice in automotive, consumer electronics, and industrial automation systems.
By supporting multiple platforms and offering rich libraries and APIs, Qt reduces development time and ensures consistent performance across hardware types.
Android Studio for Embedded Android Development
Android Studio, the official IDE for Android applications, is also applicable in the embedded world, especially for devices running the Android OS like smart TVs, automotive dashboards, or IoT devices.
It supports Java, Kotlin, and C++, enabling cross-language development. Its visual layout editor allows developers to design interfaces without writing UI code manually.
Android Studio integrates directly with the Android SDK, giving access to a wide range of libraries for device interaction, communication protocols, and system monitoring.
On-device debugging is another major benefit. Developers can connect physical devices to inspect performance, profile resource usage, and fix issues on the fly.
Git integration, emulator support, and deployment to Google Play or private app stores further extend its utility. However, apps developed in Android Studio for embedded systems must be optimized for hardware limitations and tailored to non-standard screen sizes and input methods.
Choosing the Right Tools for Your Embedded Project
Selecting the right tools for Embedded Software Development depends on several factors. These include the target hardware, the required real-time capabilities, resource constraints, and the nature of the end application.
Progressive Robot recommends that development teams assess each tool’s scalability, compatibility, and learning curve before adopting it into their workflow. An embedded medical device has vastly different requirements than a consumer smart speaker, so tool selection must align with technical goals and compliance needs.
Development speed, debugging support, and ease of testing should also be taken into account. An integrated IDE that can automate builds, run simulations, and log hardware responses is invaluable in saving time and reducing risk.
Conclusion
Embedded Software Development plays a critical role in the functioning of modern technology. As embedded devices become more complex, the demand for efficient development tools continues to rise.
Using robust IDEs like Visual Studio, Eclipse, or Android Studio, paired with powerful platforms such as Qt, ARM mbed, or FreeRTOS, developers can accelerate their work and build high-performing embedded applications.
Whether you’re developing for industrial automation, automotive control systems, or smart consumer devices, selecting the right combination of tools and frameworks is essential to project success. With thoughtful planning and tool selection, developers can overcome the unique challenges of embedded software and deliver responsive, stable, and efficient systems.

