Blockchain in Payments is revolutionizing the way we handle financial transactions in the digital age. Over the last decade, the payments industry has undergone a dramatic transformation, shifting from cash and cheques to mobile wallets, digital banking, and seamless online transfers. What once demanded a trip to the bank can now be accomplished instantly with a smartphone. As technology advances, the question in 2025 is no longer if finance will go digital — it’s about how fast and how far. Amid economic uncertainty, regulatory shifts, and sustainability challenges, blockchain is emerging as one of the most promising innovations shaping the future of payments.
As of 2025, however, the financial sector faces uncertainty. Questions loom about whether this exponential growth in digital finance will continue or decelerate. A mix of economic crises, evolving regulations, and sustainability concerns all play a role in shaping the future of online transactions. Amid these challenges, one technology has emerged as both bold and reliable in redefining the payment process — blockchain in payments.
What Is Blockchain Technology in Payments?

At its core, blockchain in payments refers to using a decentralized digital ledger to record, validate, and execute financial transactions. Instead of relying on centralized banks or payment processors, blockchain technology allows users to transfer funds directly to one another, with verification handled by a network of distributed computers (or “nodes”).
This disintermediation eliminates the need for middlemen, saving both time and money while enhancing transaction transparency. In traditional systems, sending money internationally can involve several banks and days of waiting. With blockchain, the same transaction can settle within seconds and at a fraction of the cost.
Whether you’re a global business or an individual sending remittances, the efficiency of blockchain payment systems has made them an increasingly attractive alternative in 2025.
Projected Growth of Digital Payments Market (2025–2030)
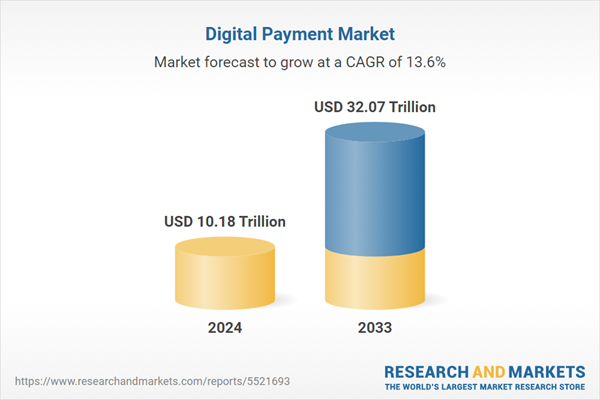
Market forecasts from financial analysts project significant growth in the digital payments market from 2025 through 2030. As blockchain technology becomes more accessible and integrated into mainstream applications, businesses and consumers alike are embracing it.
Reports indicate that blockchain in payments will play a pivotal role in this evolution, potentially contributing to trillions in transaction value across both developed and emerging markets. Central banks, fintech firms, and traditional institutions are investing heavily in blockchain infrastructure, signaling a promising future for its continued adoption.
Key Benefits of Using Blockchain in Payments

The benefits of blockchain in payments are numerous, and they address many of the long-standing challenges in traditional banking systems:
Speed: Cross-border payments that once took 3–5 business days can now be completed in seconds or minutes using blockchain.
Cost-efficiency: By eliminating intermediaries, blockchain slashes transaction fees — often from 3–7% to under 1%.
Transparency: Every transaction is recorded on a public, immutable ledger, reducing fraud and increasing accountability.
Availability: Blockchain payments are not restricted by weekends or bank hours. Transactions can occur 24/7/365.
Accessibility: Users do not need a bank account to send or receive payments, making financial inclusion more achievable.
Security: Decentralized and encrypted systems make blockchain payments less vulnerable to breaches and centralized failures.
Here’s a direct comparison for clarity:
| Feature | Traditional Systems | Blockchain-Based Payments |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | 1–5 days (cross-border) | Seconds to minutes |
| Fees | 3–7% | Often less than 1% |
| Transparency | Low | High |
| Availability | Bank hours | 24/7/365 |
| Security | Centralized, breach-prone | Decentralized, encrypted |
| Trust Model | Third-party institutions | Distributed consensus |
Types of Blockchain-Based Payment Systems
By 2025, blockchain technology has evolved into a diverse ecosystem. Depending on use case, businesses can choose from a range of blockchain in payments solutions:
1. Cryptocurrency Payments
Users can pay using cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), or stablecoins like USDC and USDT. These are ideal for reaching customers in countries with restrictive banking systems or unstable local currencies.
2. Wallet-to-Wallet Transfers
These peer-to-peer payments allow direct transfer from one digital wallet to another, commonly used in ride-sharing, freelancing, and digital marketplaces. The simplicity of scanning a QR code or entering a wallet address is revolutionizing instant payments.
3. Smart Contract Payments
Smart contracts are blockchain programs that execute automatically when pre-defined conditions are met. They’re useful for automating freelancer payments, renewals, and revenue sharing, and eliminate the need for human intervention.
4. Stablecoin Payments
Because they’re tied to fiat currencies, stablecoins avoid the volatility of cryptocurrencies. Businesses increasingly use them for international payroll, invoice settlements, and cross-border trade payments.
5. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
CBDCs are government-backed digital currencies built on blockchain infrastructure. They combine the reliability of fiat with the speed of decentralized tech. Countries are now piloting and deploying CBDCs to modernize their economies.
How the Blockchain Payment Process Works: Step-by-Step
Understanding how blockchain in payments operates can help businesses and individuals adopt the technology with confidence:
User Initiates a Payment: The process starts with a user sending funds via a digital wallet like MetaMask or Coinbase Wallet. Businesses can embed wallet functionalities into their apps.
Transaction is Broadcasted to the Network: It’s then picked up by blockchain nodes to verify authenticity.
Transaction Is Confirmed: Validation occurs through consensus algorithms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake.
Entry Is Added to the Ledger: Once verified, the transaction is permanently recorded.
Recipient Gets Paid: Funds reflect in the recipient’s wallet almost immediately.
Optional Tracking: Apps can provide real-time updates using APIs and blockchain explorers.
Use Cases of Blockchain in Payments
1. Remittances
International money transfers are faster and cheaper with blockchain. No more delays or unnecessary intermediary fees.
2. Retail and eCommerce
Thousands of online and in-store retailers now accept crypto payments. Merchants benefit from reduced fees, faster settlement, and lower fraud risks.
3. Business-to-Business (B2B) Transactions
Smart contracts automate supply chain payments, invoice management, and cross-border transfers with zero delays or discrepancies.
4. Micropayments
Blockchain makes sending small amounts of money viable — ideal for content pay-per-use models, tipping, or usage-based services.
5. Freelancer & Gig Economy
Workers get paid instantly, bypassing the traditional banking system. Platforms like Sablier now allow real-time streaming payments.
6. Charity and Aid Distribution
Organizations like the UN use blockchain to transparently distribute funds and aid to those in need, particularly in crisis zones.
Challenges in Blockchain Payment Adoption
Despite the advantages, blockchain in payments faces a few obstacles:
Regulatory Uncertainty: Global rules vary. In some nations, blockchain payments are legal and encouraged; in others, they face restrictions.
User Experience: Complex wallet setups and cryptographic keys can be intimidating for non-tech users.
Price Volatility: Cryptocurrencies fluctuate dramatically, affecting purchasing power. Stablecoins help mitigate this, but are still gaining traction.
Limited Merchant Adoption: Until more platforms accept blockchain payments, adoption remains niche.
Irreversibility: Incorrect transactions cannot be reversed — a hurdle for some users.
How to Build a Blockchain Payment Solution
Launching a blockchain in payments platform requires vision, planning, and the right technical team.
1. Define Your Use Case
Start by identifying what problem you’re solving — P2P transfers, crypto checkout, or enterprise-grade payments.
2. Select the Right Blockchain
Choose based on speed, scalability, and cost. Ethereum for smart contracts, Solana for speed, or a private blockchain for more control.
3. Partner with a Development Firm
If you don’t have in-house expertise, partner with a blockchain-focused development firm like Progressive Robot. They handle the architecture, integrations, smart contract development, and ensure secure deployment.
4. Launch and Iterate
After testing, launch your platform and continually refine it based on user behavior, feedback, and performance analytics.
The Future of Blockchain in Payments
The future of blockchain in payments is bright. Major banks are testing and deploying blockchain technology to enhance efficiency and transparency. Meanwhile, decentralized finance (DeFi) is gaining popularity, offering banking services without the banks.
Stablecoins are becoming central to cross-border trade and payroll. As artificial intelligence (AI) gets integrated into payment systems, fraud detection, risk assessment, and transaction monitoring will become even smarter.
From seamless user experiences to global financial inclusion, blockchain is already changing how the world sends, receives, and processes money — and it’s just the beginning.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How does blockchain assist with payments?
Blockchain enables peer-to-peer transactions without banks. It’s fast, affordable, and borderless.
2. Is blockchain for payments safe to use?
Yes, blockchain uses strong encryption and decentralized validation. Always use reputable platforms and safeguard your credentials.
3. What is a stablecoin?
A stablecoin is a type of cryptocurrency pegged to a stable asset, like the US dollar or euro. Because its value doesn’t fluctuate wildly, it’s perfect for day-to-day transactions, salary payments, and cross-border transfers.
4. What is positive about blockchain payments?
From a business standpoint, blockchain in payments offers significant advantages. Transactions are faster, fees are lower, and transfers can happen globally without relying on conventional banking systems. It’s also highly transparent and reduces the risk of fraud.
5. What are the downsides of using blockchain money transfers?
Some challenges include the volatility of non-stable cryptocurrencies, lack of user-friendly interfaces, regulatory uncertainty, and limited mainstream adoption. However, improvements are continuously being made to address these issues.
6. Will blockchain substitute normal payments?
While it’s not likely to completely replace traditional payment systems in the near future, blockchain in payments is becoming a strong complement. As adoption increases and barriers lower, blockchain may become the default for many types of transactions.
Conclusion: The Era of Blockchain in Payments Has Arrived
We are living in a time when digital transformation is not just a trend—it’s a necessity. In this landscape, blockchain in payments is emerging as a revolutionary force, redefining how money moves across the globe. It offers solutions to decades-old problems in financial systems: sluggish transaction speeds, high fees, lack of transparency, and exclusion of the unbanked.
From retail and remittances to business payments and charitable giving, blockchain technology is already proving its worth in real-world applications. While challenges like regulation, volatility, and user education remain, they are steadily being addressed through innovation, collaboration, and strategic adoption.
Whether you are a startup, enterprise, nonprofit, or government, now is the time to explore how blockchain in payments can enhance your financial operations. With partners like Progressive Robot, organizations can turn this technology into powerful, secure, and scalable solutions tailored to their needs.
As AI, DeFi, and blockchain converge, the future of payments looks smarter, faster, and more inclusive than ever before. The transformation is underway — and blockchain is leading the charge.
