Introduced in 2015 by Vitalik Buterin, Ethereum has become a crucial part of the decentralized world. It lets developers build and run various decentralized applications (DApps) while automating operations. This guide explores Ethereum Blockchain Architecture, including its key parts, how decisions are made, and future upgrades.
Ethereum Blockchain Architecture supports smart contracts and DApps, making it a leader in web3 technology. By understanding its structure, you can see why it remains a top choice for developers. Let’s dive into its main components and how they work together.
Overview of Ethereum

Ethereum is a decentralized platform where developers create apps without central control. Unlike Bitcoin, which focuses on transactions, Ethereum Blockchain Architecture allows code execution. Its native cryptocurrency, Ether (ETH), powers the network and pays for services.
The platform uses distributed databases, ensuring transparency and security. Smart contracts run automatically when conditions are met, removing the need for middlemen. This makes Ethereum Blockchain Architecture ideal for trustless applications.
Ethereum continues to evolve, with upgrades improving speed and efficiency. Its flexibility and strong community support keep it at the forefront of blockchain innovation.
Key Components of Ethereum Blockchain Architecture
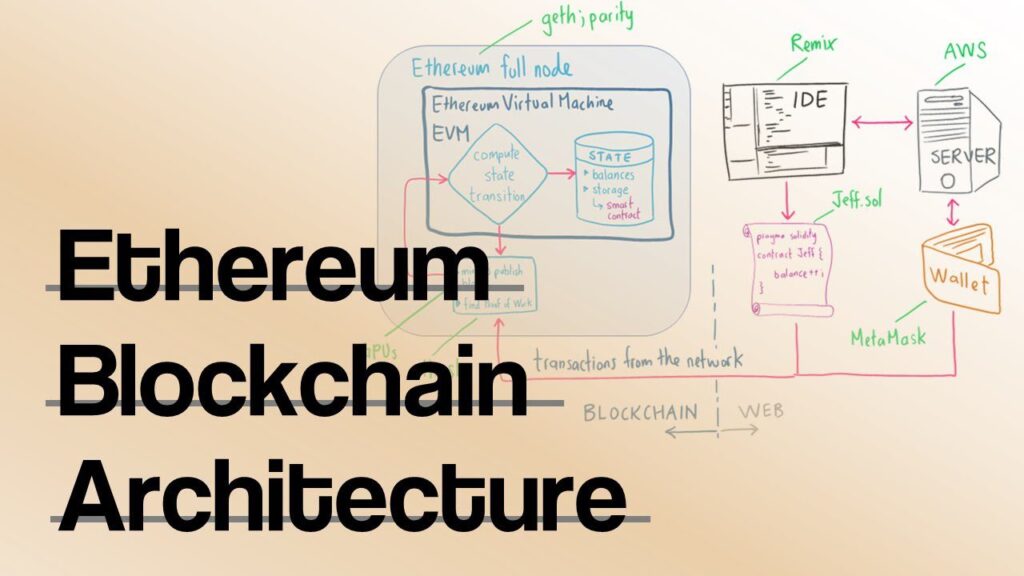
The Ethereum Blockchain Architecture consists of several important parts that work together. The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is the core, executing smart contracts securely. It ensures code runs the same way on all devices, maintaining consistency.
Ether (ETH) is the fuel of the network, used for transactions and staking. Gas fees prevent spam by charging users for computational work. Transactions include sender and receiver details, ETH amounts, and optional smart contract data.
Nodes maintain the network by validating transactions. Full nodes store the entire blockchain, while light nodes rely on others for data. Archive nodes keep a complete history, useful for research and analytics.
Consensus Mechanisms in Ethereum Blockchain Architecture

Ethereum originally used Proof of Work (PoW), where miners solved puzzles to validate transactions. However, PoW consumed too much energy, leading to scalability issues. Now, Ethereum Blockchain Architecture is shifting to Proof of Stake (PoS).
In PoS, validators stake ETH to create new blocks, improving speed and reducing energy use. This upgrade, called Ethereum 2.0, aims to make the network more sustainable. The change also enhances security by making attacks more expensive.
The move to PoS is a major step forward for Ethereum Blockchain Architecture. It addresses key challenges while keeping the network decentralized and efficient.
Smart Contracts and Decentralized Applications

Smart contracts are self-executing agreements written in code. They run on the EVM, automating processes without intermediaries. Developers use languages like Solidity and Vyper to create them.
Decentralized applications (DApps) operate on Ethereum Blockchain Architecture, offering various services. Popular examples include Uniswap for trading and MakerDAO for lending. These apps rely on smart contracts to function trustlessly.
If you need DApp development services, Progressive Robot can help. Our team builds secure, efficient solutions for industries like finance, logistics, and more. We ensure your project meets the highest standards.
Common Challenges in Ethereum Blockchain Architecture

Scalability is a major issue, as Ethereum can handle only a limited number of transactions per second. High demand leads to network congestion and expensive fees. The shift to PoS and sharding aims to solve this problem.
Energy consumption was another concern under PoW, but PoS reduces it significantly. User experience also needs improvement, as blockchain technology can be complex for beginners. Regulatory uncertainty adds another layer of difficulty.
Despite these challenges, Ethereum Blockchain Architecture continues to evolve. Upgrades and community efforts ensure it remains a leading platform for innovation.
Future Trends and Developments

Ethereum 2.0 is the biggest upcoming change, introducing PoS and sharding for better performance. Layer 2 solutions like Rollups will further reduce fees and increase speed. These improvements make Ethereum Blockchain Architecture more user-friendly.
DeFi and NFTs are growing rapidly, creating new opportunities. More industries are adopting Ethereum for secure, transparent solutions. Continuous research ensures the network stays ahead in the web3 space.
Progressive Robot stays updated with these trends, offering cutting-edge development services. Whether you need smart contracts or DApps, we deliver top-quality solutions tailored to your needs.
Conclusion
Ethereum Blockchain Architecture has transformed the digital world with its decentralized approach. Its support for smart contracts and DApps makes it a powerful platform for innovation. As upgrades roll out, Ethereum will become even faster and more efficient.
Looking for expert smart contract development? Progressive Robot provides secure, reliable solutions for your blockchain projects. We help you build and optimize applications for success in the evolving web3 landscape. Contact us today to get started!

